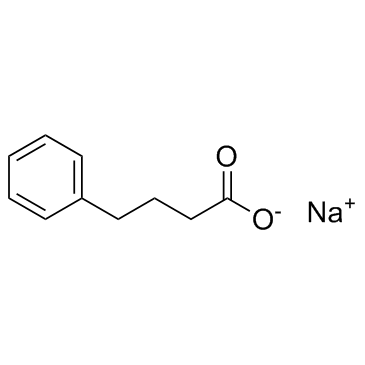
Sodium Phenylbutyrate
CAS No. 1716-12-7
Sodium Phenylbutyrate( Benzenebutanoic Acid | NSC 657802 | TriButyrate )
Catalog No. M12616 CAS No. 1716-12-7
Sodium Phenylbutyrate is a transcriptional regulators that act by altering chromatin structure via the modulation of HDAC activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 34 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 78 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 130 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSodium Phenylbutyrate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSodium Phenylbutyrate is a transcriptional regulators that act by altering chromatin structure via the modulation of HDAC activity.
-
DescriptionSodium Phenylbutyrate is a transcriptional regulators that act by altering chromatin structure via the modulation of HDAC activity.(In Vitro):Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate (Sodium phenylbutyrate) is an inhibitor of HDAC, inhibits the growth of NSCLC Cell Lines at 2 mM. Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate in combination with ciglitizone results in enhanced growth arrest of cancer cells. Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate (Sodium phenylbutyrate; 0-5 mM) inhibits ASFV infection in a dose-dependent manner. Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate also inhibits the ASFV late protein synthesis and disrupts the virus-induced H3K9/K14 hypoacetylation status. Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate and Enrofloxacin act synergistically to abolish ASFV replication. Addition of Bafilomycin A1 results in accumulation of LC3II, whereas Benzenebutyric acid (4-PBA) substantially reduces this accumulation. LPS decreases the level of p62, whereas Benzenebutyric acid reverses this decrease upon LPS stimulation for 48 h. The percentage of cells with LPS-induced AVOs is increased at 48 h, whereas Benzenebutyric acid significantly reduces this percentage. Specifically, the percentage of cells with AVOs decreases from 61.6% to 53.1% upon Benzenebutyric acid treatment, supporting that Benzenebutyric acid inhibits LPS-induced autophagy. As a positive control for autophagy inhibition, bafilomycin A1 is used. The percentage of cells with LPS-induced AVOs is reduced by bafilomycin A1 treatment. The decreased OC area and fusion index observed after Benzenebutyric acid treatment are not observed with knockdown of ATG7. Inhibition of NF-κB using BAY 11-7082 and JSH23 reduce the LC3 II level upon LPS stimulation and completely abolish the inhibitory effect of Benzenebutyric acid on LPS-induced effects.(In Vivo):LPS induces significant bone loss and decreases bone mineral density (BMD), bone volume (BV/TV), and trabecular thickness (Tb. Th) compared with PBS alone, whereas trabecular space (Tb. Sp.) is increased. Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate (Sodium phenylbutyrate) attenuates LPS-induced bone loss. Treatment with Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate increases BMD, BV/TV, and Tb. Th. compared with LPS alone, in addition to decreasing the enlargement of Tb. Sp., but no change is observed when mice are treated with Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate alone. OC.S/BS as assessed by TRAP staining is also significantly reduced when Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate is administered to LPS-treated mice. However, OC.N/BS tends to decrease, although not with statistical significance, when mice are treated with Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate and LPS. These results indicate that the effect of Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate on OC from LPS-treated mice is to reduce its size rather than number. Consistent with these findings, a marker of bone resorption in vivo, serum CTX-1 which is elevated by LPS treatment is decreased when Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate administered to LPS-injected mice. However, co-treatment with Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate do not significantly affect the levels of serum ALP and osteocalcin, 2 markers of bone formation in vivo, compared with LPS alone. Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate also reduces the LPS-induced rise in serum MCP-1, indicating that Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate decreases systemic inflammation induced by LPS.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsBenzenebutanoic Acid | NSC 657802 | TriButyrate
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetHDAC
-
RecptorHDAC
-
Research AreaMetabolic Disease
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1716-12-7
-
Formula Weight186.18
-
Molecular FormulaC10H11NaO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityWater: 30 mg/mL (161.13 mM); DMSO: 8 mg/mL (42.96 mM)
-
SMILESO=C([O-])CCCC1=CC=CC=C1.[Na+]
-
Chemical Namesodium 4-phenylbutanoate
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Burrage LC, et al. Mol Genet Metab. 2014 Sep-Oct;113(1-2):131-5.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Vorinostat
A potent HDAC inhibitor, inhibits the activities of HDAC1 and HDAC3 with IC50 of 10 nM and 20 nM, respectively.
-
Pimelic Diphenylamid...
A slow, tight-binding inhibitor of class I HDACs.
-
QTX125
QTX125 (QTX-125) is a novel potent, selective HDAC6 inhibitor, displays excellent selectivity over other HDACs.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


